What is a Surge Protective Device (SPD)?
In today’s technology-driven world, electrical devices and systems are integral to both daily life and industrial operations. However, sudden voltage spikes—commonly known as power surges—can damage sensitive electronics, disrupt workflows, and lead to costly downtime. This is where a Surge Protective Device (SPD) plays a critical role. In this article, we’ll explain what an SPD is, how it works, and why it’s essential for safeguarding your equipment.
Understanding Power Surges
Power surges are abrupt, short-lived increases in voltage that exceed the standard flow of electricity in a circuit. These surges can originate from external sources (e.g., lightning strikes, utility grid fluctuations) or internal sources (e.g., large appliances turning on/off, faulty wiring). Even minor surges, if repeated, can degrade electronic components over time.
What is a Surge Protective Device?
A Surge Protective Device (SPD), also called a surge suppressor or lightning arrester, is a safety component designed to protect electrical systems and equipment from voltage spikes. It acts as a “gatekeeper,” diverting excess voltage away from connected devices and limiting the surge to a safe level.
SPDs are used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to protect everything from household appliances to complex machinery, data centers, and telecommunications systems.
How Does an SPD Work?
SPDs detect voltage spikes and respond almost instantaneously (in nanoseconds) to redirect the excess energy. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Detection: The SPD monitors the electrical circuit for voltage exceeding the safe threshold.
- Diverting Excess Energy: When a surge occurs, the SPD creates a low-resistance path to channel the excess voltage to the ground or neutral line.
- Clamping Voltage: The device ensures the voltage supplied to connected equipment remains within a safe range.
Modern SPDs often use components like metal oxide varistors (MOVs), gas discharge tubes, or avalanche diodes to achieve this protection.

Types of Surge Protective Devices
SPDs are categorized based on their application and installation point:
- Type 1 (Class I): Installed at the main service entrance to protect against external surges (e.g., lightning strikes).
- Type 2 (Class II): Mounted at subpanels or distribution boards to shield against residual surges and internal switching transients.
- Type 3 (Class III): Point-of-use devices (e.g., power strips) for direct protection of individual equipment.
For comprehensive protection, a layered approach combining all three types is often recommended.
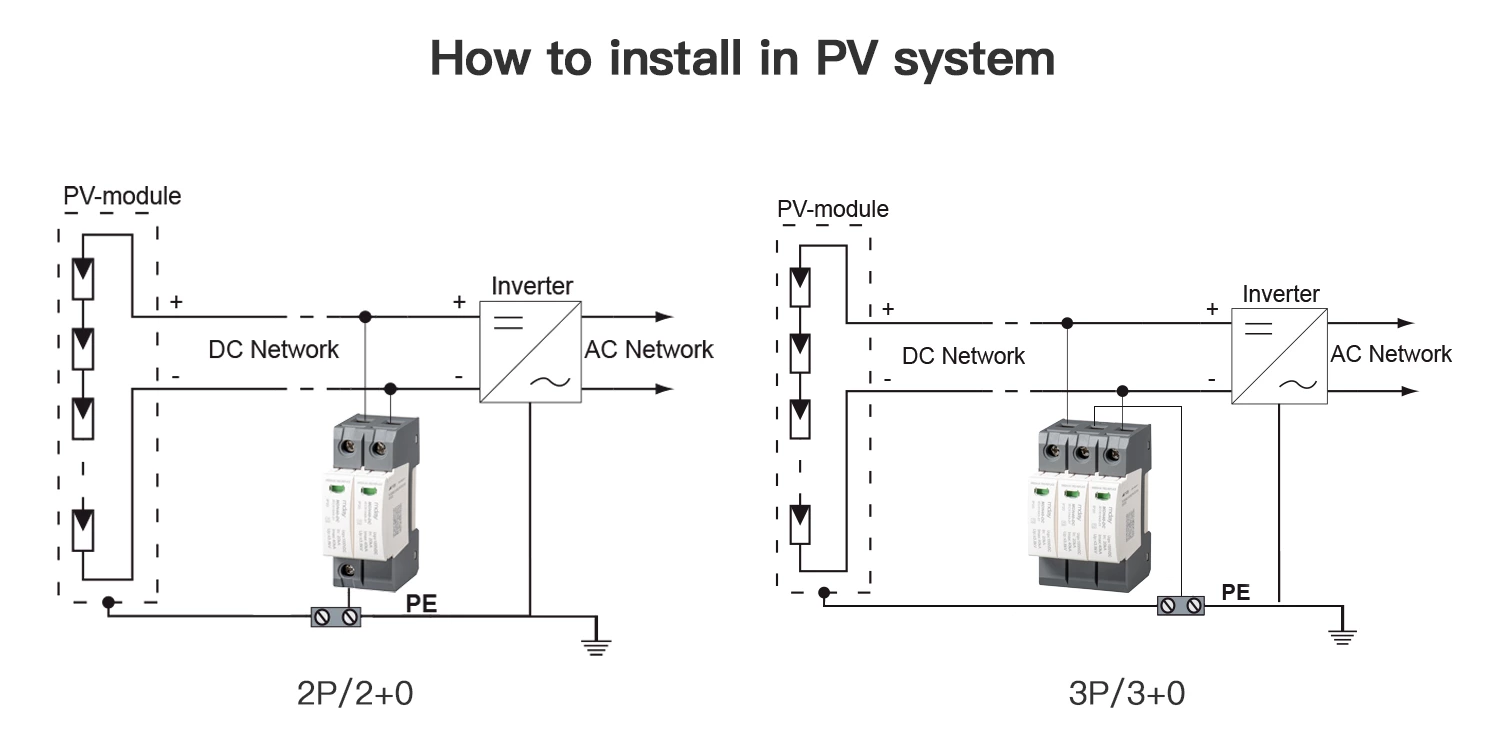
Why Do You Need an SPD?
- Prevent Equipment Damage: Surges can fry circuits, corrupt data, and shorten the lifespan of electronics.
- Reduce Downtime: Critical systems, such as servers or production lines, stay operational during electrical disturbances.
- Cost Savings: Avoid expensive repairs or replacements caused by surge-related failures.
- Safety: Mitigate fire risks associated with overheating from power surges.
Choosing the Right SPD
When selecting an SPD, consider:
- Voltage Rating: Matches your electrical system’s requirements.
- Energy Absorption Capacity (measured in joules): Higher ratings handle larger surges.
- Response Time: Faster response (nanoseconds) ensures better protection.
- Certifications: Look for compliance with standards like UL 1449, IEC 61643, or IEEE C62.41.
Conclusion
A Surge Protective Device is not just an optional accessory—it’s a vital investment for anyone relying on electrical and electronic systems. Whether you’re a homeowner, a business owner, or an industrial operator, integrating SPDs into your infrastructure ensures reliability, safety, and long-term savings.
At [Your Company Name], we specialize in high-quality surge protection solutions tailored to your needs. Protect your assets today—contact us or visit our Google-powered independent website to explore our range of SPDs and expert guidance.




