Temperature Controller
What is a Temperature Controller?
A temperature controller is a device that regulates temperature in a system, maintaining it at a desired setpoint.
It works by comparing the measured temperature from a sensor (like a thermocouple or RTD) to the desired setpoint and then adjusts heating or cooling elements to achieve and maintain that temperature.

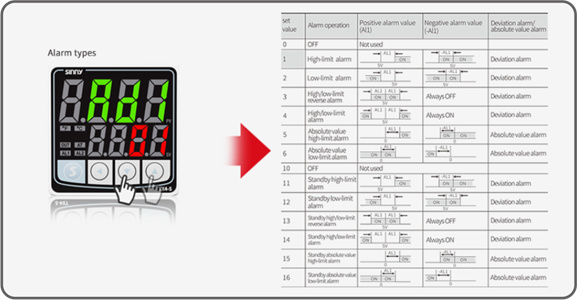
Why Are Temperature Controllers Important?
Temperature controllers are essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety in both industrial equipment and consumer products. They are needed in any application where a specific process temperature is required to be stable.
For example, in the food industry, temperature controllers are critical for preserving food safety standards as they help to maintain a consistent and safe temperature range in refrigeration equipment to prevent food spoilage and contamination.
Types of Temperature Controller
There are two types of temperature control: open loop control and closed loop control. Open loop control is a type of control system in which the output of the system is not monitored or fed back to the input.
This means that the system is not self-regulating and is prone to error over time. Closed loop control, on the other hand, is a type of control system in which the output is monitored and fed back to the input.
This allows the system to make adjustments as needed in order to keep the output within a desired range. This makes the system self-regulating and much less prone to error over time.
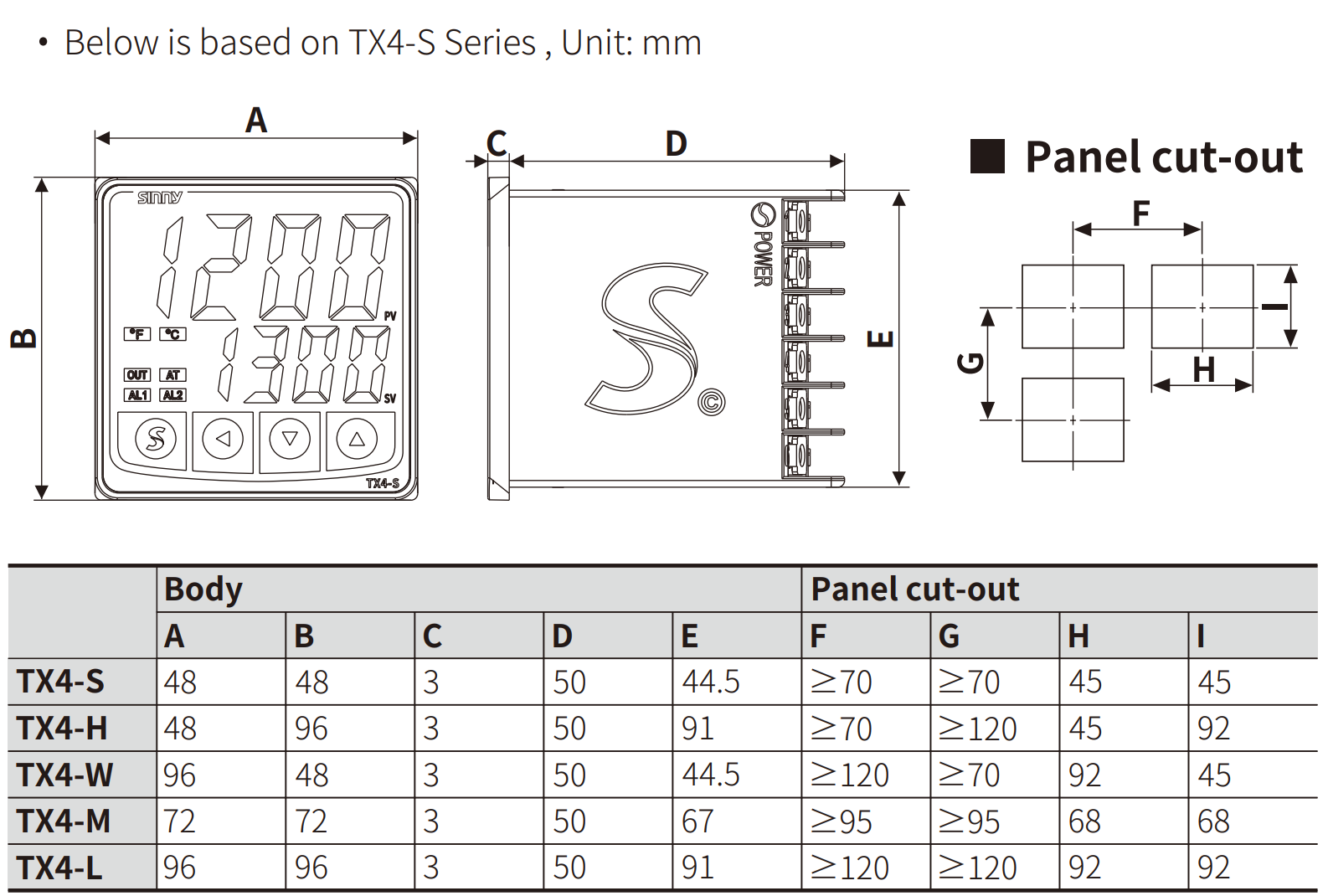
Panel Cutouts : Standard Industrial Size
The opening dimensions for a 96×96mm meter are 92×92mm (width×height).
The opening dimensions for a 48×96mm meter are 45×92mm (width×height).
The opening dimensions for a 96×48mm meter are 92×48mm (width×height).
The opening dimensions for a 48×48mm meter are 45×45mm (width×height).
The opening dimensions for a 72×72mm meter are 68×68mm (width×height).
PID vs On/OFF Temperature Controllers


| Feature | On/Off Temperature Controller | PID Temperature Controller |
|---|---|---|
| Control Mechanism | Heater fully ON or OFF based on temperature | Continuous adjustment of power based on PID algorithm |
| Accuracy | Lower; causes temperature swings (overshoot/undershoot) | High; maintains stable and precise temperature |
| Complexity | Simple operation, easy to set up | Complex; requires tuning of proportional, integral, derivative parameters |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Applications | Basic heating, where swings are acceptable | Precise processes such as medical sterilization, industrial ovens |
Temperature Controller More Related Articles

A temperature controller is a device that monitors and regulates temperature to a setpoint. Using a sensor (like a thermocouple or RTD), it compares measured temperature to the target and adjusts heating or cooling via outputs (relay, SSR, or analog) using control methods such as on/off or PID.

A PID temperature controller regulates heat by continuously calculating error (setpoint minus measured temperature) and adjusting output using three terms: Proportional (current error), Integral (accumulated past error), and Derivative (predicted future error) for stable, accurate control.











