Understanding Rocker Switches

A rocker switch is an electrical switch that operates using a pivot mechanism, enabling toggling between two positions. This design gives rocker switches their distinctive "rocking" appearance when pressed. Their simplicity and ergonomic design make rocker switches a favored choice across various industries.
Rocker switches are available in several types, each serving unique functions. Familiarity with these types is vital for informed decision-making:
- Single Pole Single Throw (SPST): The most basic type, allowing simple on/off control of a single circuit.
- Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT): Connects to one of two circuits, providing versatility with three terminals and toggling between two states.
- Double Pole Single Throw (DPST): Controls two circuits simultaneously, ideal for high-power applications.
- Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT): A complex switch that manages two circuits with two distinct positions, often used in advanced electronic configurations.
Due to their diverse functionalities, rocker switches find applications in various settings. In residential environments, they're commonly utilized in light fixtures and appliances for easy device control. In the automotive sector, rocker switches operate features like headlights, windscreen wipers, or auxiliary lights. Furthermore, industrial applications employ rocker switches in machinery, providing reliable control in demanding environments.
Understanding the types and applications of rocker switches is crucial for selecting the best model for your requirements, ensuring effective performance and user satisfaction.
Types of Rocker Switches
Single-Pole Rocker Switch
Controls a single circuit, commonly found in household lighting and appliances.
Advantages: Simple design, cost-effective, easy installation.
Disadvantages: Limited to basic on/off control.
Double-Pole Rocker Switch
This switch can control two separate circuits, making it ideal for higher voltage applications like industrial equipment.
Advantages: Increased power handling, suitable for larger systems.
Disadvantages: More expensive than single-pole switches.
Momentary Rocker Switch
Maintains its state only while pressed, often used for start/reset functions in machinery.
Advantages: Ideal for temporary actions.
Disadvantages: Not suitable for applications requiring a constant on/off state.
Illuminated Rocker Switch
Equipped with built-in lighting, offering visual indication for power status, commonly used in automotive and aerospace contexts.
Advantages: Enhances usability by indicating operational status.
Disadvantages: Slightly more complex wiring.
Non-Illuminated Rocker Switch
Lacks built-in lights and is used in simpler applications where indication isn't necessary.
Advantages: Cost-efficient, simple, reliable.
Disadvantages: No visual feedback during use.
How to Choose the Right Rocker Switch
Having comprehended the types of rocker switches, the next step involves selecting the appropriate one for your needs. This selection process is crucial for ensuring functionality and safety in your application. Here are key considerations to guide your choice:
- Load Requirements: Clearly define the electrical load your switch will manage. Ensure that the switch's current and wattage ratings meet or exceed the requirements of the devices it will control.
- Rated Voltage: Confirm that the rocker switch is compatible with your voltage system, whether for standard household use (typically 120V) or industrial applications requiring higher voltages.
- Size: The switch's physical dimensions are important. Ensure it fits the panel or mounting location, allowing for adequate spacing and accessibility for user operation.
- Environmental Factors: If the switch will be exposed to outdoor conditions or wet environments, choose models that offer waterproof or dustproof ratings (such as IP65 or IP67) to prevent moisture ingress and corrosion.
- Safety Certifications: Look for switches that comply with relevant safety standards (such as UL, CE, or RoHS certifications). These indicators confirm that the product underwent rigorous testing for electrical safety and reliability.
Decision-Making Checklist
- Determine load and voltage specifications
- Measure available installation space
- Assess environmental conditions
- Verify safety certifications
- Consider aesthetic and ergonomic factors
Step-by-Step Wiring Instructions
Proper wiring is essential for ensuring safe and effective operation. This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to wire various types of rocker switches, along with helpful tips to avoid common mistakes.
Tools and Materials Needed:
- Rocker switch (SPST, SPDT, DPST, or DPDT)
- Wire stripper
- Screwdriver (flat and Phillips)
- Electrical tape
- Multimeter (for testing)
- 12-14 gauge wire (depending on the circuit)
Wiring Diagrams for Different Switch Types:
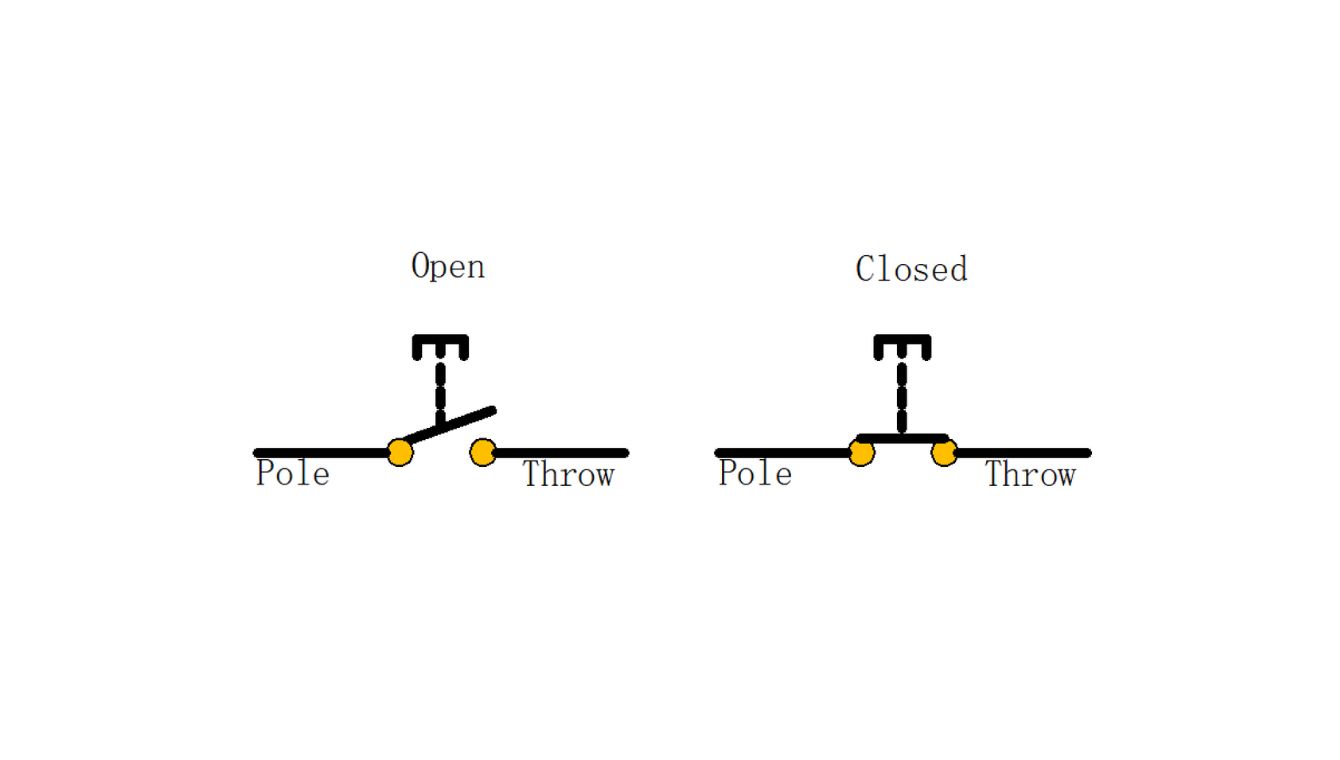
Single Pole Single Throw (SPST)
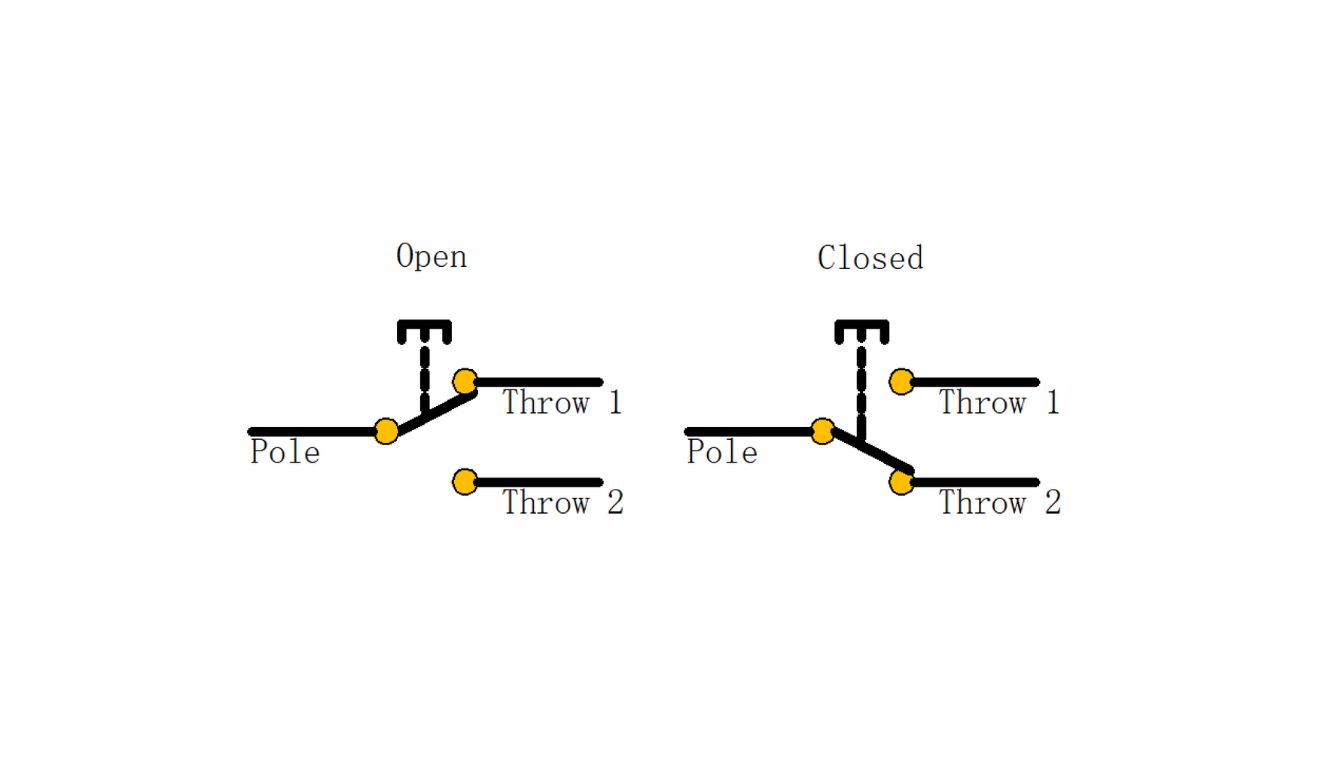
Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT)
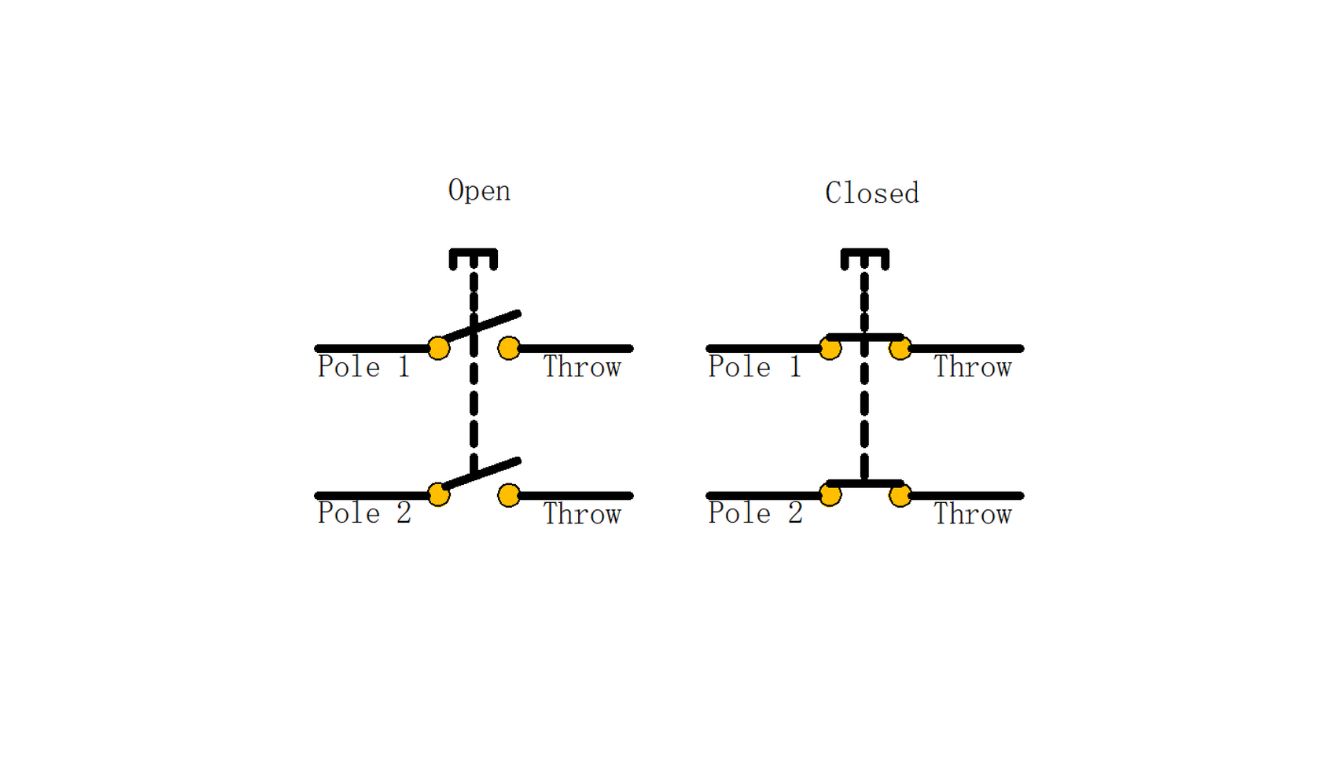
Double Pole Single Throw (DPST)
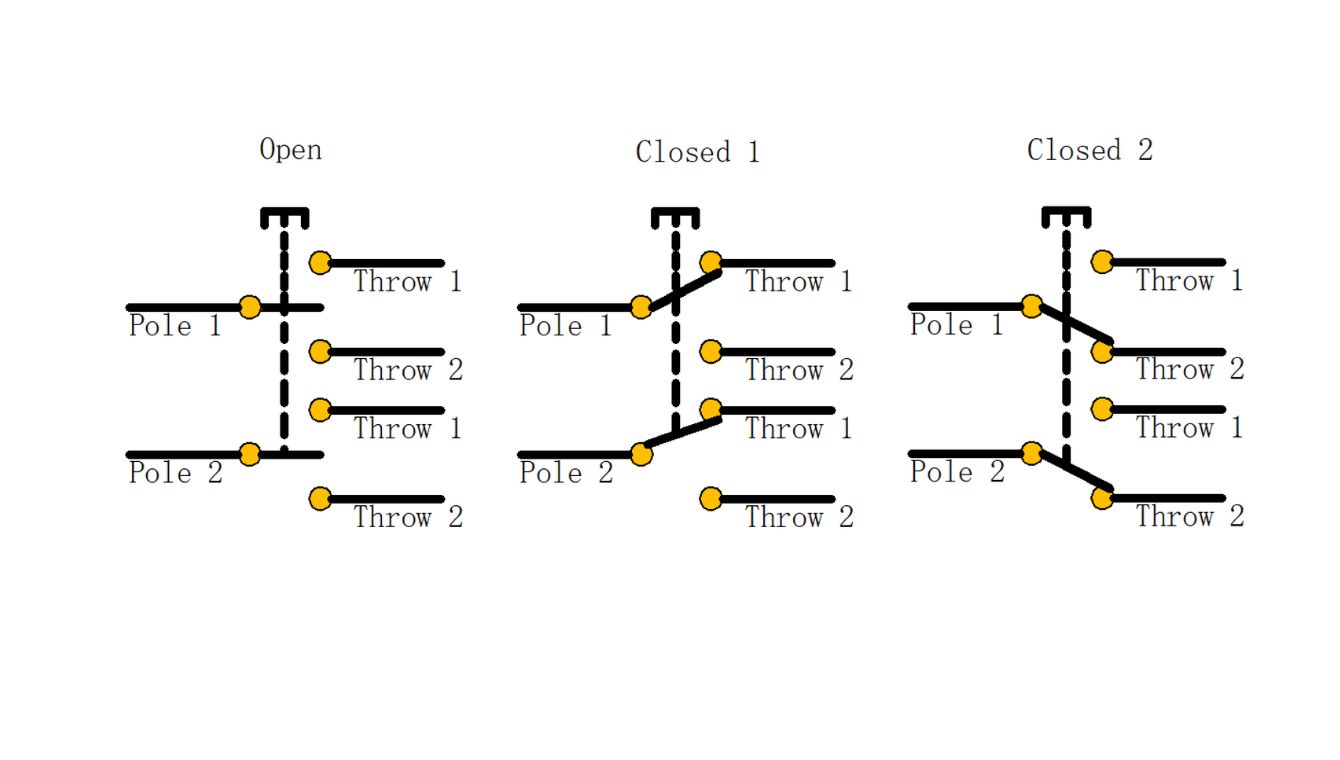
Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Reversing the polarity of the wire connections.
- Using the incorrect gauge wire, which may lead to overheating.
- Failing to secure connections, which can result in shorts.
Safety First: Always ensure your circuit is off before starting any wiring work.
Common Troubleshooting Tips
Understanding common issues and knowing how to troubleshoot can save time and prevent unnecessary replacements.
Typical Problems:
- Switch Not Responding: The switch fails to activate the connected device.
- Flickering Lights: The connected light source dims or blinks intermittently.
- Physical Damage: Signs of wear, such as cracks or a stuck toggle.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the Power Supply: Confirm that the power source is functional by testing it with another device.
- Inspect Connections: Ensure all wired connections to and from the switch are secure and free from corrosion.
- Test the Switch: Use a multimeter to check for continuity. If there's no continuity, the switch may require replacement.
- Clean the Switch: Dust and debris can hinder performance. Gently clean around the mechanism with compressed air.
Buying Guide for Rocker Switches
When selecting a rocker switch for your project or application, several key specifications and considerations should guide your decision.
- Current Rating: Determine the typical load your switch will manage; options usually range from 3A to 20A or more.
- Voltage Rating: Common ratings include 12V, 24V, and 120V, but verify your equipment to ensure compatibility.
- Design & Size: Consider illuminated, non-illuminated, and weatherproof options suitable for indoor and outdoor use.
- Material and Durability: Look for switches constructed from high-quality materials, such as thermoplastic or metal.
For recommended brands, Carling Technologies and NKK Switches are reputable manufacturers. For household applications, brands like GE and Leviton provide reliable options. Price ranges can vary significantly, from $2 for budget options to $30+ for specialized switches.
Buying Checklist
- Verify current and voltage ratings.
- Assess the physical design and size constraints.
- Review material for durability and application suitability.
- Consider brand reputation and customer reviews.
- Establish a budget, keeping in mind the balance between cost and quality.
